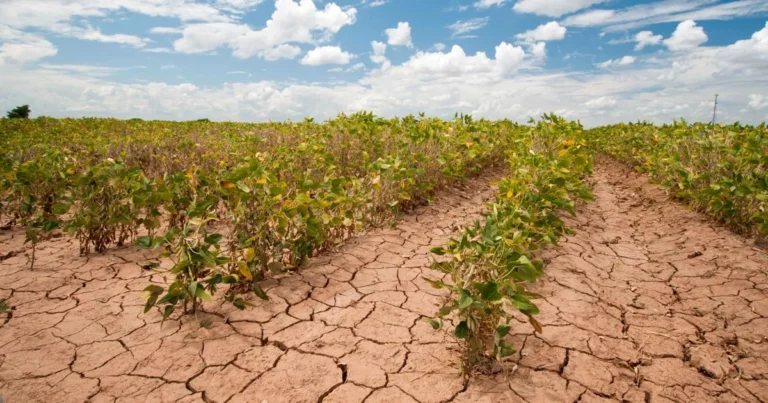
Climate patterns play a pivotal role in shaping agricultural practices, influencing everything from crop selection to irrigation strategies. Understanding the nuances of these patterns is crucial for farmers to optimize productivity while mitigating risks associated with climate variability. In this blog post, we’ll explore how this effect influence agricultural practices in different regions, highlighting adaptation strategies and innovative approaches employed by farmers.
Climate Patterns and Crop Selection:
In regions characterized by distinct climate patterns, such as temperate, arid, or tropical climates, farmers carefully select crops based on their suitability to prevailing conditions. For example, in arid regions with limited water availability, farmers may prioritize drought-resistant crops like millet or sorghum. Conversely, in temperate climates with ample rainfall, farmers might opt for crops like wheat or barley that thrive in moist conditions.
Water Management Strategies:
Climate patterns also dictate water management strategies employed by farmers. In regions prone to droughts or erratic rainfall, farmers implement water-saving techniques such as drip irrigation or rainwater harvesting to conserve precious water resources. Additionally, in areas susceptible to flooding due to heavy rainfall, farmers may adopt drainage systems or raised beds to prevent waterlogging and ensure proper soil aeration.
Seasonal Variability and Planting Schedules:
The variability in climate patterns, including seasonal shifts and extreme weather events, significantly impacts planting schedules and crop cycles. Farmers must adapt their planting schedules to align with optimal growing conditions and avoid potential risks posed by climatic fluctuations. For instance, in regions prone to late frosts, farmers may delay planting until after the last frost date to minimize frost damage to sensitive crops.
Pest and Disease Management:
Climate patterns also influence pest and disease pressure in agricultural systems. Warmer temperatures and increased humidity levels can create favorable conditions for pest proliferation and disease outbreaks. As a result, farmers in such regions may implement integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including crop rotation, biological control methods, and the judicious use of pesticides, to mitigate pest and disease pressures while minimizing environmental impact.
Adaptation Strategies and Innovation:
In response to shifting climate patterns, farmers are increasingly adopting innovative practices and technologies to enhance resilience and adaptability. This includes the adoption of drought-tolerant crop varieties, precision agriculture techniques, and climate-smart farming practices tailored to local climatic conditions. Furthermore, advancements in agricultural research and technology are enabling farmers to leverage weather forecasting tools and data-driven decision-making to optimize resource allocation and mitigate climate-related risks.
Conclusion:
Climate patterns exert a profound influence on agricultural practices, shaping crop selection, water management strategies, planting schedules, pest and disease management, and adaptation strategies. By understanding and adapting to local climate patterns, farmers can optimize productivity, enhance resilience, and contribute to sustainable agricultural development. Continued investment in research, innovation, and farmer education is essential to empower farmers with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate the complexities of climate variability and ensure food security in the face of changing climatic conditions.